As we age, maintaining mobility and bone health becomes essential for preserving independence and quality of life. Conditions like osteoporosis and arthritis, along with the natural decline in bone density and joint flexibility, can make staying active more challenging. However, with the right strategies and expert advice from an orthopedist, it’s possible to keep bones strong and joints healthy well into your senior years. In this article, we’ll explore common orthopedic issues and practical tips for maintaining mobility and bone health.
Common Orthopedic Issues in Older Adults

As we age, our bones and joints become more vulnerable to various conditions. Understanding the most common orthopedic issues can help you take preventive action and manage symptoms effectively.
1. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition that weakens bones by reducing their density, making them more prone to fractures. This is especially common in older adults, particularly postmenopausal women, due to the loss of estrogen, which plays a crucial role in maintaining bone density.
- Why seniors are at risk: Bone loss accelerates with age, increasing the risk of fractures, especially in the hips, spine, and wrists.
- Impact: Osteoporotic fractures can lead to long-term disability, chronic pain, and a significant reduction in mobility.
2. Arthritis
Arthritis is another common issue affecting older adults. There are several types, but osteoarthritis (the “wear and tear” type) is the most prevalent.
- Osteoarthritis: Occurs when the cartilage that cushions the joints wears down, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced movement.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune condition that causes joint inflammation, leading to pain and deformity.
- Symptoms and Impact: Arthritis causes pain, swelling, and stiffness, making it difficult to move joints and affecting overall mobility and independence.
3. Joint and Muscle Injuries
As we age, we are more susceptible to injuries such as sprains, strains, and fractures due to weakened muscles, balance issues, and decreased flexibility.
- Impact of aging on recovery: Aging slows the body’s ability to heal, making it harder to recover from injuries.
- Increased risk: Balance problems and muscle weakness increase the likelihood of falls and related injuries.
Orthopedist-Recommended Strategies for Maintaining Bone Health

Maintaining strong bones is crucial for avoiding fractures and other complications that can limit mobility.
1. Nutrition for Bone Health
A healthy diet rich in essential nutrients supports bone density and strength.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: These are the key nutrients for bone health. Calcium strengthens bones, while vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium.
- Calcium-rich foods: Dairy products, leafy greens, almonds, and fortified cereals.
- Vitamin D sources: Sunlight exposure, fortified foods, and supplements if necessary.
- Supplementation: For those who struggle to meet their dietary needs, supplements may be recommended, especially for individuals with lactose intolerance or limited sun exposure.
2. Weight-Bearing Exercises
Regular physical activity, particularly weight-bearing exercises, is one of the best ways to maintain bone density.
- Recommended exercises: Walking, hiking, stair climbing, and strength training help strengthen bones and muscles.
- Balance and flexibility: Activities like yoga and tai chi improve balance and flexibility, reducing the risk of falls that could lead to fractures.
3. Avoiding Bone-Damaging Habits
Certain lifestyle habits can accelerate bone loss and weaken the body’s support structure.
- Smoking: Smoking is linked to lower bone density and higher fracture risk.
- Excessive alcohol: Alcohol can interfere with calcium absorption and weaken bones over time.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Staying inactive reduces bone strength, making bones more fragile and prone to fractures.
Orthopedist-Recommended Strategies for Maintaining Mobility

Keeping joints and muscles healthy is key to staying mobile and independent.
1. Exercise for Joint Health
While exercise is important for bone health, it is equally vital for maintaining joint mobility and flexibility.
- Low-impact exercises: Swimming, cycling, and yoga are ideal for maintaining joint flexibility and reducing arthritis pain without placing too much strain on the joints.
- Strengthening exercises: Building muscle around the joints helps support movement and reduces strain on the joints.
2. Managing Weight to Protect Joints
Carrying excess weight places additional stress on the joints, particularly the hips, knees, and ankles.
- Reducing joint pressure: Maintaining a healthy weight decreases the strain on weight-bearing joints, which can prevent or reduce the symptoms of osteoarthritis.
- Balanced diet: A healthy diet, combined with regular physical activity, can help manage weight and improve overall joint health.
3. Protecting Joints from Overuse
Joints are vulnerable to wear and tear, especially with repetitive movements or improper technique during physical activities.
- Proper technique: Using the correct form during exercise and daily activities helps prevent overuse injuries.
- Supportive devices: Orthotic devices, braces, and supportive footwear can provide additional protection for vulnerable joints, particularly during activities like walking or sports.
Medical Interventions and Treatments for Orthopedic Issues
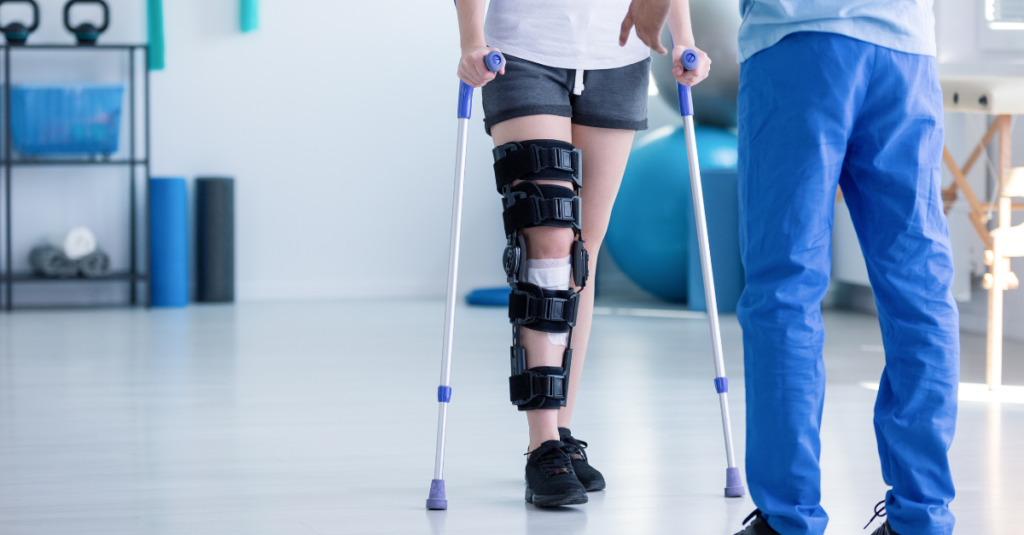
For those experiencing more severe bone and joint problems, medical interventions may be necessary.
1. Medications
Various medications can help manage symptoms of arthritis and osteoporosis.
- For arthritis: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids can reduce inflammation and pain.
- For osteoporosis: Bisphosphonates and hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can slow bone loss and improve bone density.
2. Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy is an effective way to improve mobility and strengthen muscles after an injury or surgery.
- Customized exercise programs: A physical therapist can create an exercise program tailored to your specific needs, helping to regain strength and flexibility in weakened areas.
- Rehabilitation after surgery: Physical therapy is often essential after joint replacement surgery to help restore function and mobility.
3. Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgery may be the best option for restoring mobility and reducing pain.
- Joint replacement: For those with severe arthritis, hip or knee replacement surgery can dramatically improve quality of life.
- Minimally invasive surgeries: These procedures offer faster recovery times and less risk than traditional surgeries, making them a preferred option for many patients.
Preventing Falls and Fractures

Falls are a major cause of fractures in older adults, particularly for those with osteoporosis.
1. Fall Prevention Strategies
Making changes to your home and daily routine can significantly reduce the risk of falls.
- Home modifications: Install grab bars, remove tripping hazards, and ensure proper lighting in frequently used areas.
- Balance exercises: Balance-focused activities like tai chi and yoga can improve stability and prevent falls.
2. Bone Density Testing
Bone density tests, such as DEXA scans, help detect osteoporosis before fractures occur.
- Who should get tested: Women over 65, men over 70, and those with risk factors should get regular bone density tests.
- Frequency: Bone density should be tested every 1-2 years for those at risk.
The Role of Regular Check-Ups with an Orthopedist
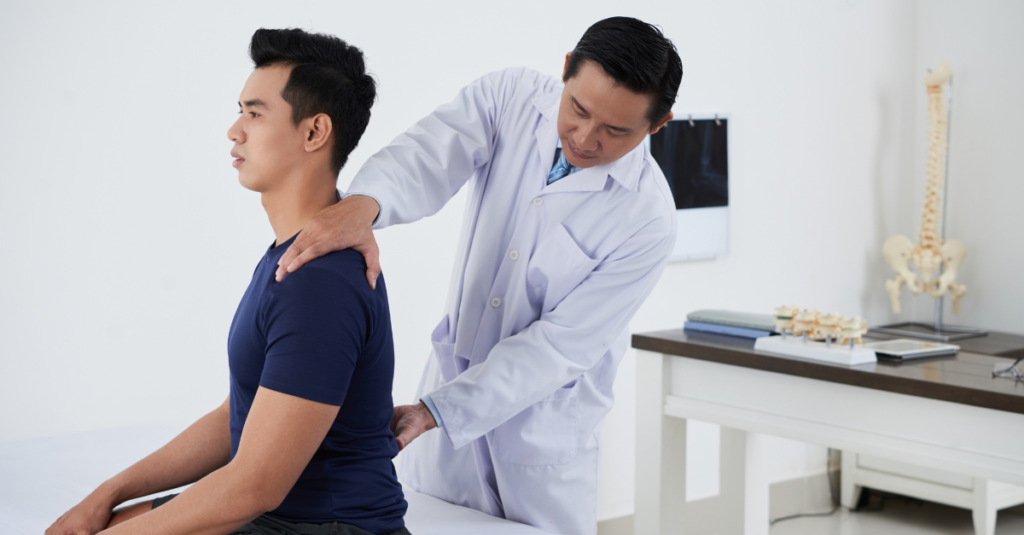
Regular visits to an orthopedist can help you stay on top of your bone and joint health.
1. Monitoring Bone and Joint Health
Routine check-ups allow an orthopedist to monitor bone density, joint function, and overall mobility.
- Early detection: Regular monitoring helps detect potential issues early, allowing for timely interventions that can prevent further deterioration.
2. Developing a Personalized Care Plan
An orthopedist can work with you to create a care plan tailored to your specific needs, helping you maintain mobility and bone health as you age.
Maintaining bone health and mobility is essential for staying active and independent as you age. With proper nutrition, regular exercise, and avoiding harmful habits, you can reduce the risk of osteoporosis, arthritis, and other orthopedic issues. Additionally, regular check-ups with an orthopedist, along with medical interventions when needed, can help you manage any bone or joint conditions and prevent future complications.
By following these expert recommendations, you can maintain your mobility, protect your bones, and enjoy a higher quality of life as you age.

