Osteoporosis, often referred to as the “silent disease,” affects millions of people worldwide, particularly older adults. It weakens bones, making them more fragile and prone to fractures, which can seriously affect health and mobility. However, with early detection and proactive measures, osteoporosis-related fractures can often be prevented. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of bone density tests, preventive strategies, and how to maintain strong bones to reduce the risk of fractures.
Understanding Osteoporosis and Its Impact
What is Osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis occurs when bones lose density and strength over time, becoming brittle and more susceptible to fractures. This condition is particularly common in older adults, especially postmenopausal women, due to hormonal changes that accelerate bone loss.
Several risk factors contribute to the development of osteoporosis, including:
- Age: Bone density decreases naturally with age.
- Gender: Women, particularly postmenopausal women, are at higher risk.
- Family history: Genetics play a role in bone density.
- Hormonal changes: Decreased estrogen in women and testosterone in men can contribute to bone loss.
- Diet and lifestyle: Lack of calcium, vitamin D, and physical activity can weaken bones.
Impact of Osteoporosis on Health
Osteoporosis significantly increases the risk of fractures, particularly in areas like the hips, spine, and wrists. These fractures can have severe consequences, including:
- Chronic pain
- Loss of mobility and independence
- Increased risk of complications: Hip fractures, for example, can lead to long-term disability and even higher mortality rates.
For these reasons, early detection and prevention are critical.
The Importance of Early Detection
Why Early Detection is Crucial
Osteoporosis progresses silently, without symptoms, until a fracture occurs. Many people are unaware they have osteoporosis until they suffer a broken bone. This is why early detection is essential—it allows for intervention before fractures happen, reducing long-term complications.
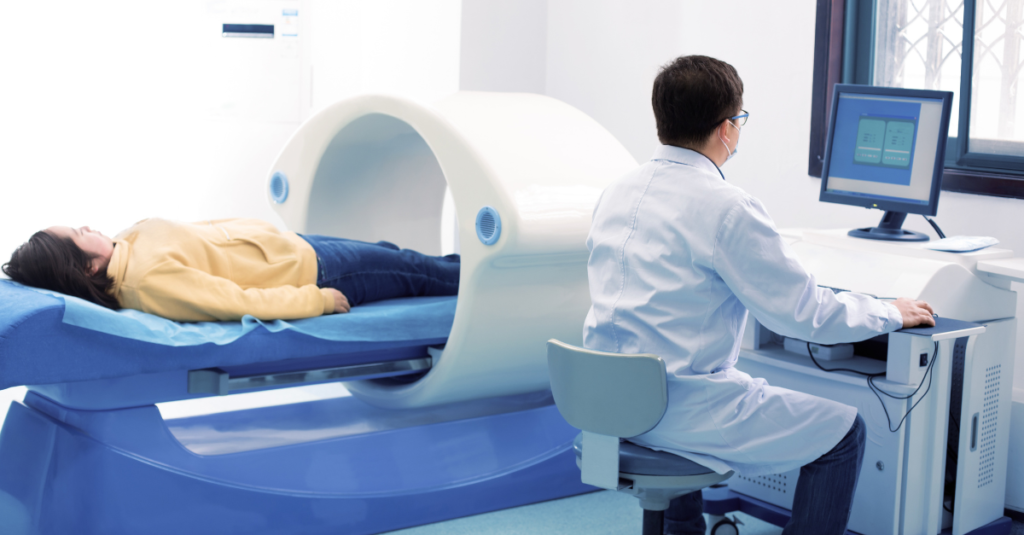
Bone Density Tests (DEXA Scan)
The most effective tool for early detection of osteoporosis is a bone density test, commonly known as a DEXA (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry) scan. This simple, painless test measures bone density in areas prone to fractures, such as the spine and hips.
Who should get tested?
- Women over 50 and postmenopausal women.
- Men with risk factors (such as a family history of osteoporosis or prolonged use of certain medications).
- Anyone who has experienced a fracture after age 50.
How results are interpreted:
- The test results are given as a T-score, which compares your bone density to that of a healthy young adult.
- A T-score of -1.0 or above is considered normal.
- A score between -1.0 and -2.5 indicates low bone mass (osteopenia).
- A score of -2.5 or lower suggests osteoporosis.
- The test results are given as a T-score, which compares your bone density to that of a healthy young adult.
Preventive Strategies to Strengthen Bones

Nutritional Strategies
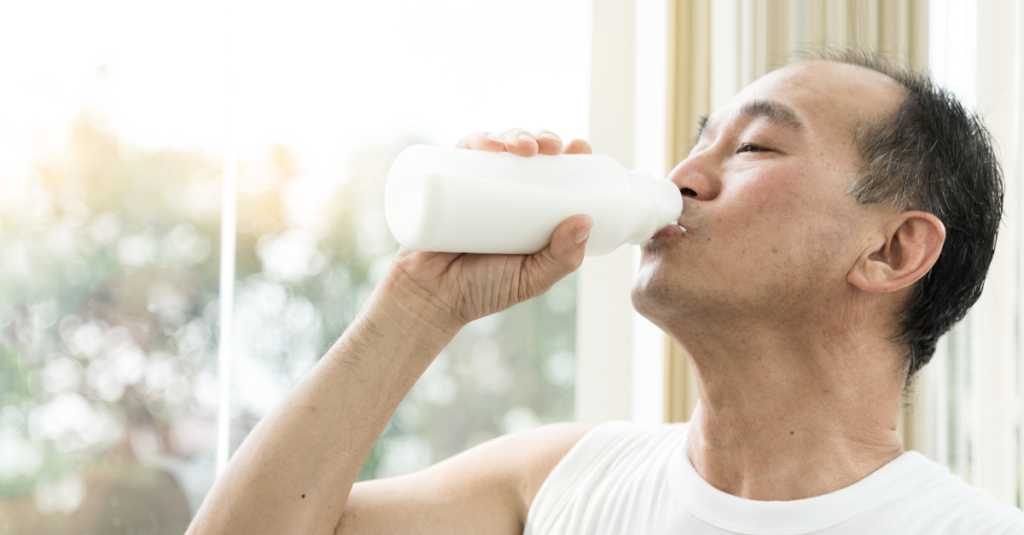
A healthy diet is key to maintaining strong bones. Two of the most important nutrients for bone health are calcium and vitamin D.
- Calcium-rich foods: Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt are excellent sources of calcium. Leafy greens, fortified cereals, and tofu can also provide calcium for lactose-intolerant people.
- Vitamin D: This vitamin helps the body absorb calcium. Sunlight is a natural source of vitamin D, but you can also get it from fortified foods or supplements.
If your diet is insufficient in these nutrients, your doctor may recommend supplements to ensure you’re getting enough calcium and vitamin D for bone health.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular physical activity strengthens bones and muscles, which can help prevent osteoporosis and fractures. The best exercises for bone health include:
- Weight-bearing exercises: Walking, jogging, and dancing help build bone density by making your bones work against gravity.
- Resistance training: Lifting weights or using resistance bands strengthens the muscles and bones.
- Balance and flexibility exercises: Yoga and tai chi improve balance, which reduces the risk of falls that could lead to fractures.
Lifestyle Changes
Certain lifestyle factors can contribute to bone loss. To keep your bones healthy:
- Avoid smoking: Smoking weakens bones by interfering with the body’s ability to absorb calcium.
- Limit alcohol intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can reduce bone formation.
- Monitor medications: Some medications, such as corticosteroids, can lead to bone loss. Work with your doctor to manage these risks.
Medical Interventions for Osteoporosis
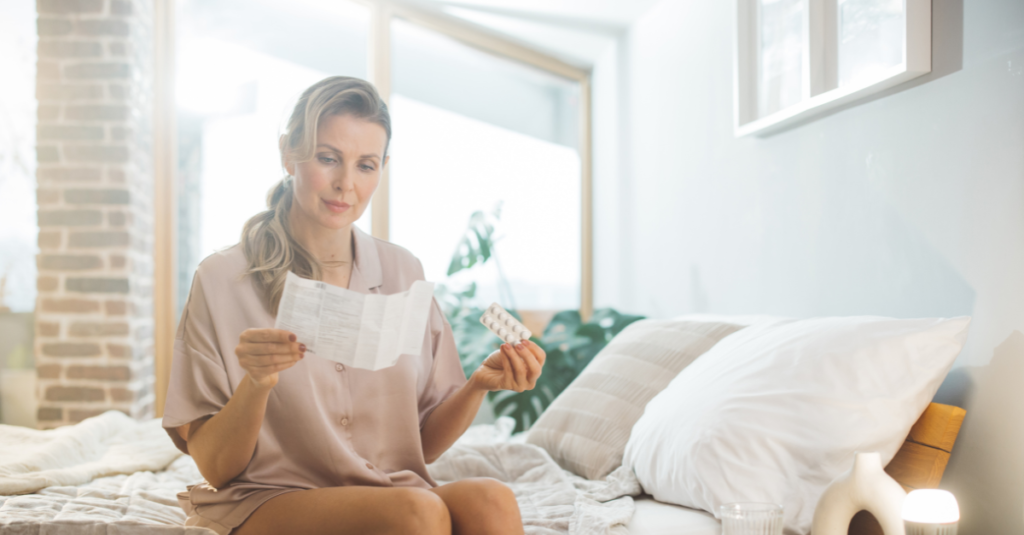

Medications for Bone Health
If you are diagnosed with osteoporosis, medications can help slow its progression and strengthen bones. Some common treatments include:
- Bisphosphonates: These medications slow down bone loss and help maintain bone density.
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT): For postmenopausal women, HRT can help restore estrogen levels and protect bone health.
- Other options: Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) and denosumab are additional treatments available for osteoporosis.
These medications are designed to prevent fractures by improving bone density and strength.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
After starting treatment, it’s important to continue regular bone density tests to monitor changes in bone health. This allows your healthcare provider to adjust your treatment plan if necessary and ensure your bones are responding to therapy.
The Role of Fall Prevention in Reducing Fracture Risk
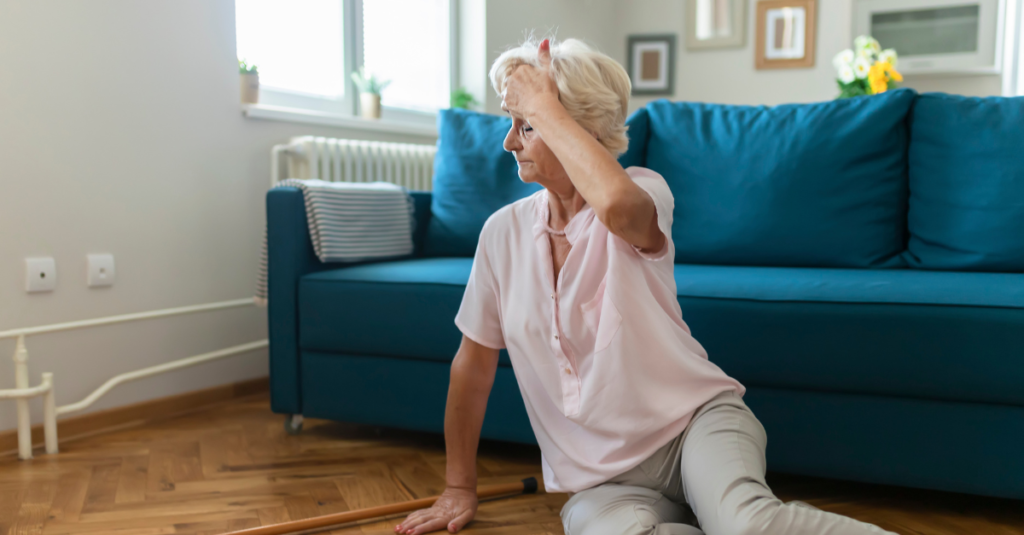

Environmental Changes
Falls are a leading cause of fractures in people with osteoporosis. Making small changes around your home can significantly reduce fall risk, such as:
- Installing grab bars in bathrooms and hallways.
- Removing tripping hazards like loose rugs or electrical cords.
- Ensuring proper lighting in frequently used areas.
Balance and Coordination Exercises
In addition to modifying your environment, exercises that improve balance and coordination can reduce the risk of falling. Activities like tai chi, yoga, or dedicated balance training help improve stability and prevent accidents that could lead to fractures.
Osteoporosis can lead to serious health complications, but early detection and proactive care can significantly reduce the risk of fractures. By undergoing regular bone density tests and following preventive strategies, you can maintain stronger bones and a higher quality of life as you age.
Key Takeaways:
- Bone density tests (DEXA scans) are essential for early detection of osteoporosis.
- Nutritional support, exercise, and lifestyle changes can strengthen bones and reduce the risk of fractures.
- Medications may be necessary to prevent further bone loss, especially in high-risk individuals.
- Fall prevention strategies, both through home safety and balance exercises, are critical for avoiding fractures.
Taking control of your bone health today can lead to a stronger, more independent future. Don’t wait—schedule a bone density test and start incorporating these preventive strategies to protect your bones and reduce your fracture risk.
